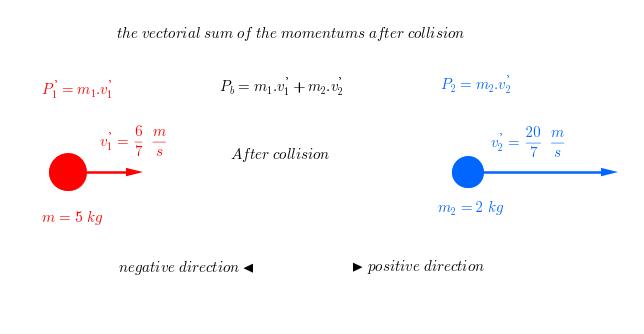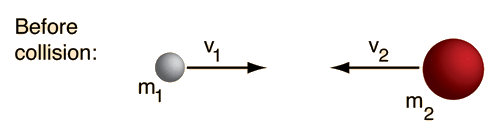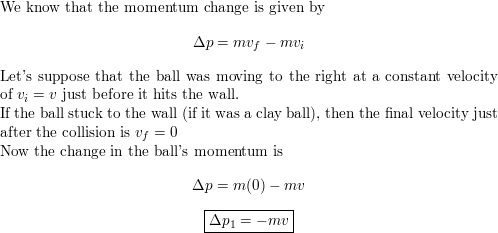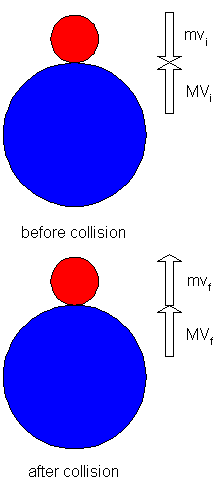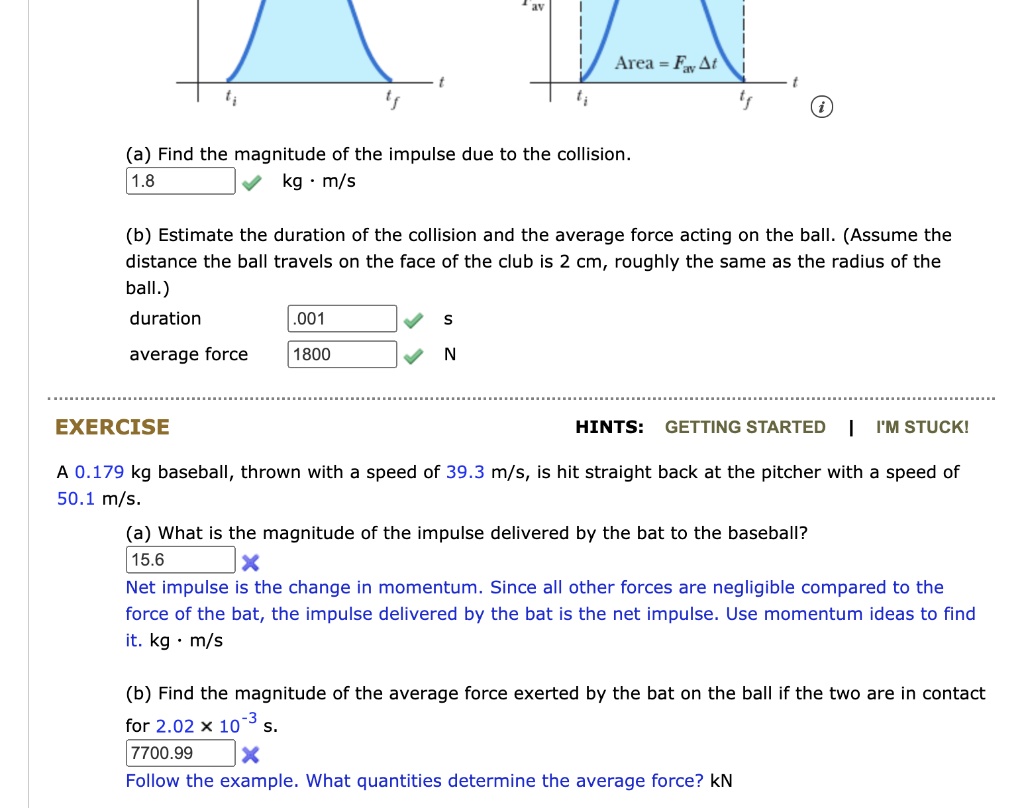
SOLVED: Area = FAt (a) Find the magnitude of the impulse due to the collision. 1.8 kg mls (b) Estimate the duration of the collision and the average force acting on the

Final Velocity in Inelastic Collisions Formula & Overview | How to Find Final Velocity - Video & Lesson Transcript | Study.com

A billiard ball moving at 5.00 m/s strikes a stationary ball of the same mass. After the collision, the first ball moves at 4.33 m/s at an angle of 30.0^o with respect

Two billiard balls each of mass 0.05 kg moving in opposite directions with speed 6 m s^-1 collide and rebound with the same speed. What is the impulse imparted to each ball

Shown in the figure is a perfect 0.04 kg ball bouncing off a floor with the same speed (|v| = 20.0 m/s) coming in as it does coming out with the angle